The Impact of 3D Printing in the Healthcare Sector
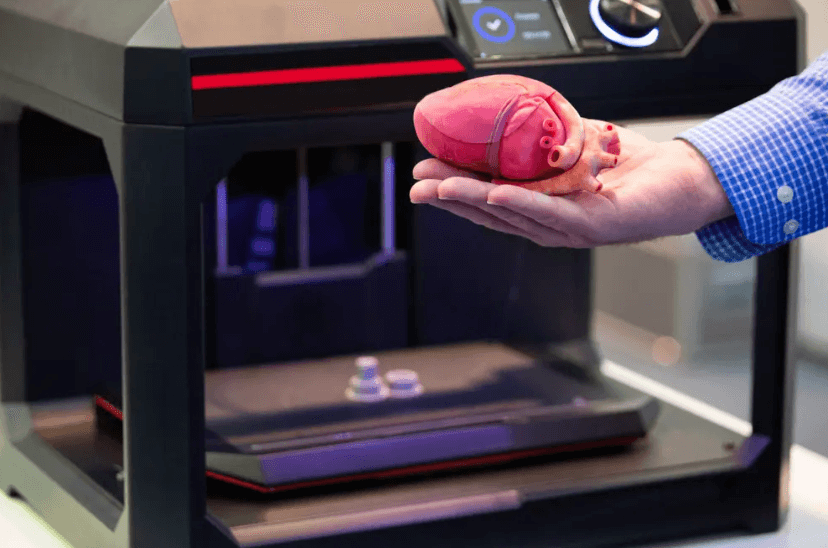
The integration of 3D printing within the healthcare sector is reshaping traditional practices. This technology facilitates the creation of bespoke medical devices and implants, tailored to individual patient needs. Such advancements promise enhanced surgical precision and improved patient outcomes. However, the journey of 3D printing in medicine is not without obstacles. Understanding the current applications and future implications of this innovation is crucial for all stakeholders involved. What lies ahead for this transformative technology?
Applications of 3D Printing in Healthcare
3D printing revolutionizes the healthcare sector by enabling the creation of customized medical devices and prosthetics tailored to individual patient needs.
Applications include the production of custom implants that fit perfectly with a patient’s anatomy, enhancing comfort and functionality.
Additionally, 3D-printed surgical guides assist surgeons in performing precise operations, thereby improving outcomes and fostering a new era of personalized medical care.
See also: The Growing Role of Automation in Manufacturing Industries
Benefits of 3D Printing for Medical Professionals and Patients
Transforming the landscape of healthcare, the integration of additive manufacturing delivers significant advantages for both medical professionals and patients alike.
This technology enhances cost efficiency by reducing material waste and production time. Additionally, it enables personalized medicine, allowing for tailored implants and prosthetics that meet individual patient needs.
Consequently, 3D printing fosters improved outcomes, streamlined processes, and greater patient satisfaction within healthcare practices.
Challenges and Future Prospects of 3D Printing in Medicine
While the potential of additive manufacturing in medicine is immense, several challenges hinder its widespread adoption.
Regulatory hurdles complicate the approval process for 3D-printed medical devices, often delaying time-to-market.
Additionally, cost implications can limit accessibility for healthcare providers and patients alike.
Addressing these obstacles is crucial for realizing the full benefits of 3D printing, paving the way for innovative solutions in healthcare.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 3D printing is revolutionizing the healthcare sector by facilitating customized medical solutions that enhance patient care and operational efficiencies. For instance, a hypothetical case involving a patient requiring a complex cranial implant illustrates this potential; a 3D-printed model of the patient’s skull can be created from imaging data, allowing surgeons to practice the procedure beforehand. As technology continues to advance, the integration of 3D printing into medical practice promises to further transform surgical outcomes and personalized treatment options.